AEM technology by Enapter
We are the pioneers and market leader of commercialized AEM Electrolyzers and at the forefront of R&D for AEM Electrolysis.
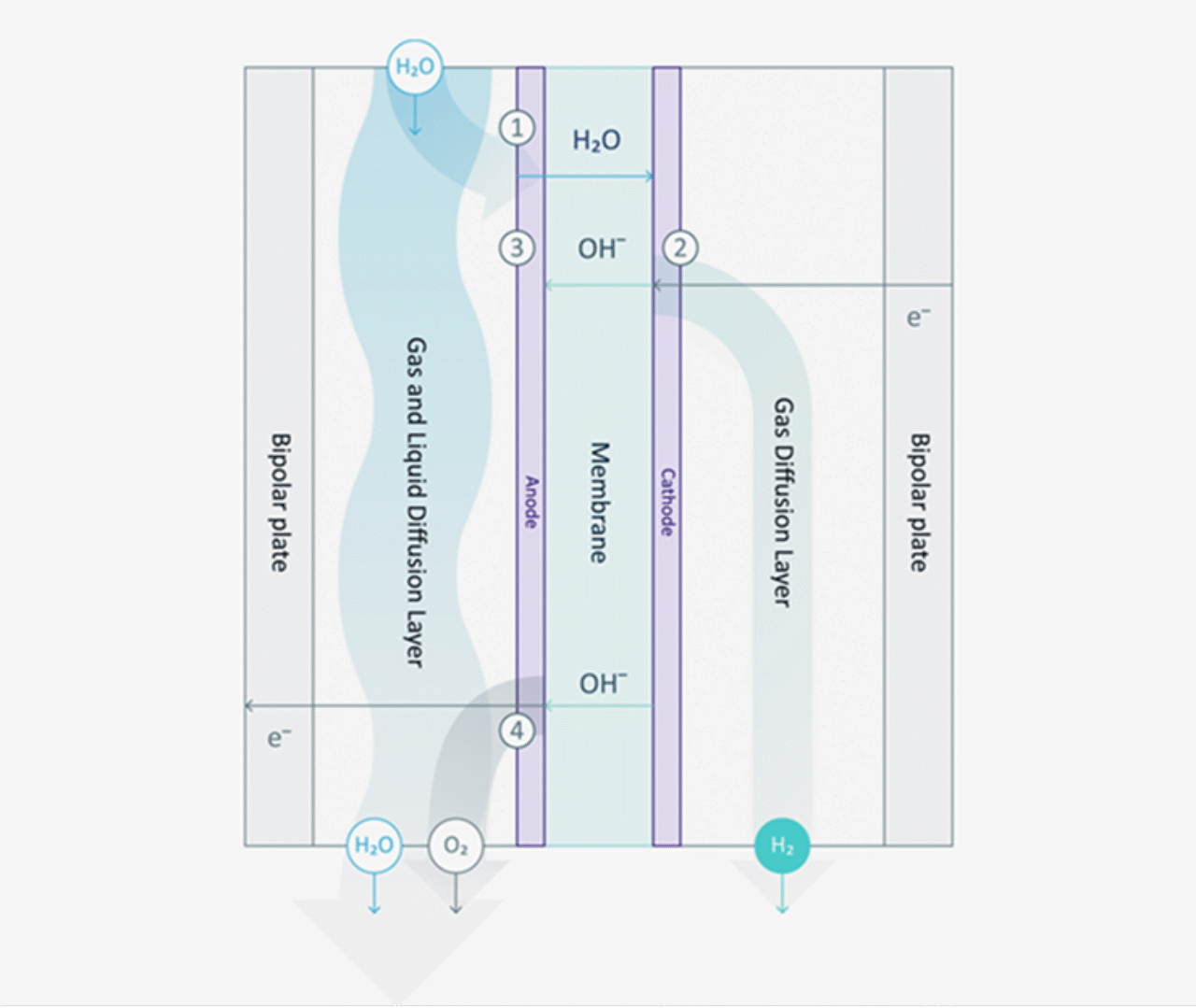
AEM (Anion Exchange Membrane) electrolysis is a type of water electrolysis technology used to produce hydrogen. Unlike proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolysis, AEM electrolysis employs a semipermeable anion exchange membrane that conducts negatively-charged ions (anions) to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
One of the main advantages of AEM electrolysis: It does not require high-cost noble metal catalysts. Instead, it can utilise low-cost transition metal catalysts. Similar to alkaline water electrolysis, the electrodes in AEM electrolysis operate in an alkaline environment. However, compared to PEM, the water requirements for AEM electrolysis are less strict and a slightly alkaline solution can be used, reducing the risk of leakage and handling issues associated with highly alkaline solutions.
Using this process, Enapter’s AEM electrolysers produce green hydrogen at a purity of 99.9% (up to 99.999% with a dryer) at a pressure of 35 bar, using only water and renewable electricity.
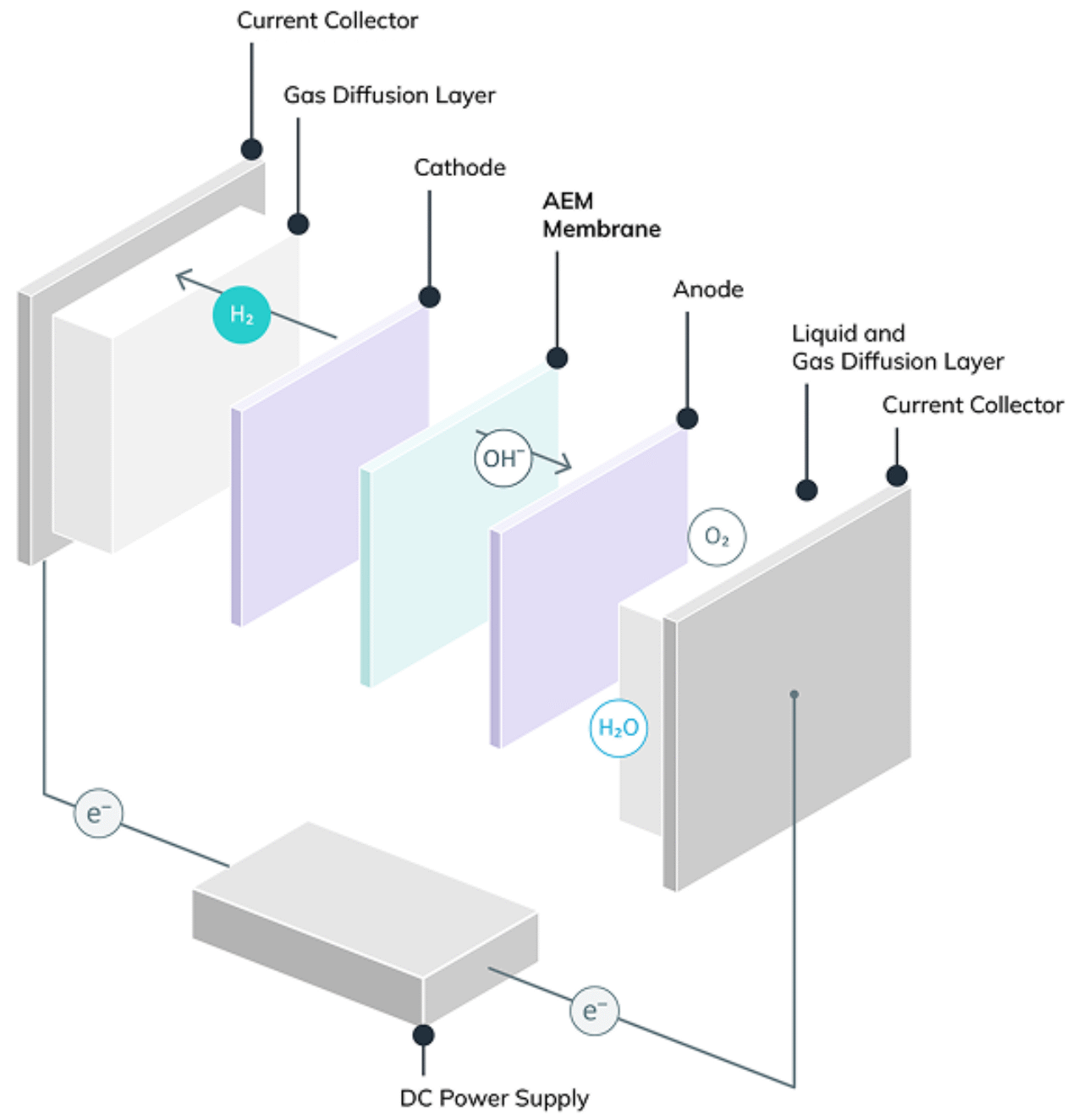
AEM technology in comparison
Unlike PEM electrolysers, AEM electrolyzers need no titanium corrosion protection, nor costly iridium. Our standardized production also leverages significant cost advantages. They likewise avoid the downsides of alkaline technology: most importantly, that it is less able to cope with the load changes and dynamics of intermittent renewable energy.
Our AEM technology combines the best of PEM and alkaline electrolyzers.
_Benefits
High operational flexibility
Its hydrogen output range matches energy fluctuations of renewable electricity sources.
Fast response time
Quick ramp-up/ramp-down in response to these changes in energy load from intermittent renewables.
Small footprint
Compact and cleverly-designed modular systems enable H2 production at exactly the scale you need.
Price stability
AEM Technology avoids the use of expensive raw materials like iridium, promoting price and supply chain stability.
Future-proofed
AEM membranes and ionomers/binders do not require the use of non-degradeable PFAS materials, enabling AEM to comply with upcoming PFAS restrictions.
_Explore Enapter’s AEM Expertise
AEM Electrolyzer technology first came to life through the Italian R&D firm ACTA S.p.A in 2009, before Enapter took over the core tech, patents and electrochemistry team in 2017.
As the world’s leading developer and manufacturer of AEM electrolyzers, Enapter builds on more than 20 years of AEM experience with a strong R&D team advancing AEM technology.
How does AEM Electrolysis work?
Dive into the mechanics of AEM electrolysis in our detailed blog article.
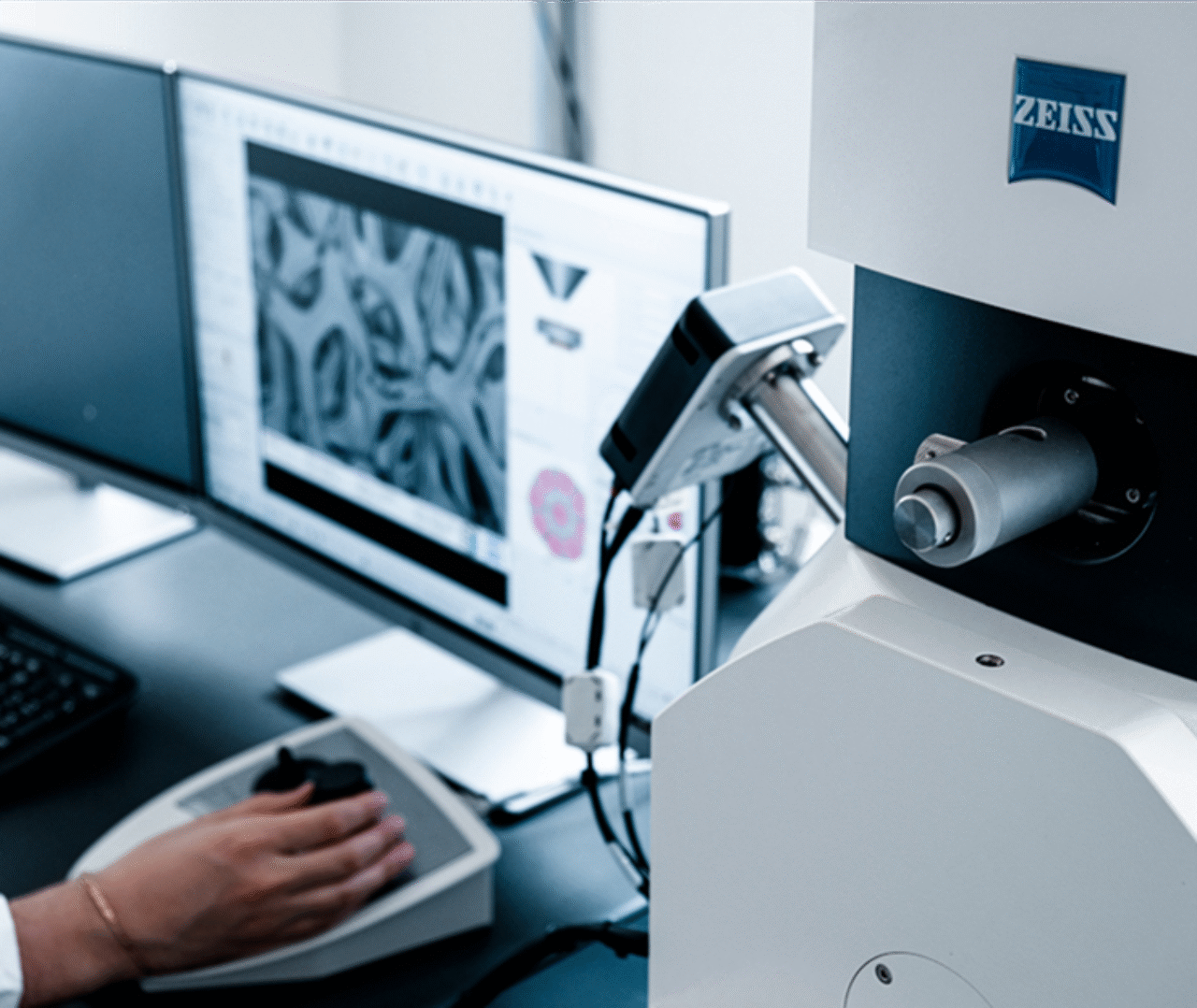
The Scanning Electron Microscope
Learn how we push the boundaries of R&D with our Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM).

Decentralized Green H2 Production
Decentralised H2 concepts that produce green hydrogen from renewable energies will be an increasingly important. How do AEM Electrolyzers fit in this study published by German Energy Agency dena?

Iridium and the Green Hydrogen Economy
Learn how a surge in demand for iridium could cause supply shortages and higher costs, potentially slowing the green hydrogen transition.

Enapter Handbook
Jump into our Handbook and discover our extensive knowledge base about AEM technology, Green Hydrogen and all technical details about our products.